The Excellence Framework Europe
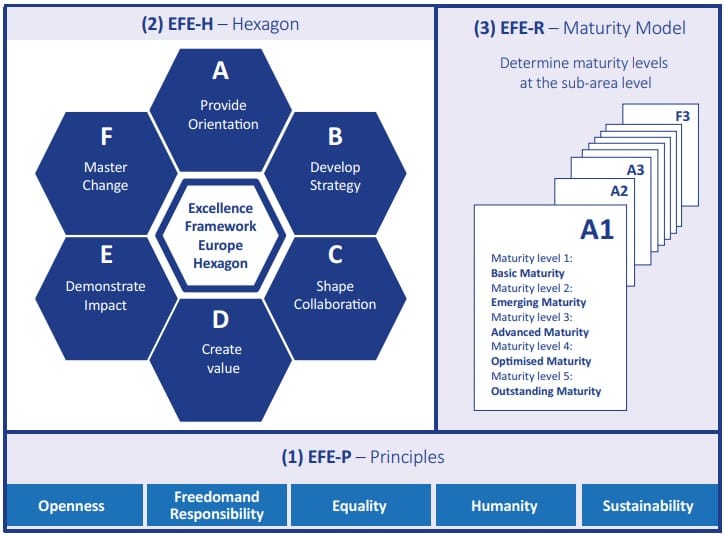
The Excellence Framework Europe consists of three central parts:
- Excellence Framework Europe – Principles
- Excellence Framework Europe – Hexagon
- Excellence Framework Europe – Maturity Model
Click on (sub)area to get more information about capability aspects.
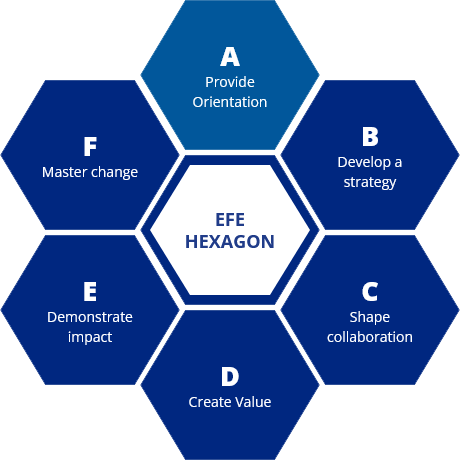
EFE Hexagon
A
Provide Orientation
A1
Creating meaning and defining futures
- Developing and anchoring understanding of meaning and purpose
- Enabling shared purpose
- Anticipating, forethinking and shaping the future
- Transforming visionary ideas into viable concepts
A2
Fostering culture and building identity
- Agreeing and embedding values
- Making culture visible and shaping relational spaces
- Living leadership and self-leadership as cultural drivers
- Fostering identity and creating commitment
A3
Embracing diversity and understanding stakeholders
- Understanding the environment, involved parties and interest groups
- Integrating social and environmental demands
- Leveraging diversity and contradictions
- Resolving obstacles and managing complexity
B
Develop a strategy
B1
Understanding the environment and organisational capabilities
- Understanding the environment and market
- Incorporating sustainability aspects
- Understanding core competencies and opportunities
- Aligning stakeholder requirements with one another
- Gaining comprehensive insights
B2
Defining strategy
- Deriving information from analyses, designing scenarios and solutions
- Defining and aligning strategic content
- Developing and refining business model(s)
- Setting strategic objectives
- Deciding and implementing strategic initiatives
B3
Implementing and reviewing strategy
- Designing consistent communication of strategy
- Cascading strategic goals
- Anchoring implementation
- Reviewing effectiveness
- Initiating adaptation of systems
C
Shape collaboration
C1
Involving stakeholders
- Segmenting stakeholders
- Attracting and engaging employees
- Acquiring and retaining customers
- Finding partners and suppliers and developing together
- Providing feedback
C2
Designing products and services
- Defining value proposition
- Designing and implementing innovation processes
- Considering the life cycle
- Assessing technologies
- Managing the value proposition portfolio
- Identifying and securing knowledge
C3
Designing structure and organisation
- Defining and delimiting added value
- Designing value creation processes
- Enabling adaptable structures
- Utilising trust and personal responsibility as design principles
- Promoting learning ability and transferring knowledge
- Balancing tensions
C4
Providing technology and resources
- Raising and providing capital
- Preparing, approving and implementing investments
- Managing and securing data, information and knowledge
- Mastering technologies and reducing complexity
- Improving and innovating simultaneously
- Shaping digital transformation
D
Create Value
D1
Attracting and inspiring customers
- Communicating customer benefits and winning customers
- Obtaining and integrating customer feedback
- Designing and improving customer experiences
- Aligning the value chain with customer needs
- Refining value proposition for specific markets and customer segments
D2
Empowering employees
- Embracing leadership as a service
- Testing new ideas and driving things forward
- Promoting lifelong learning
- Promoting feedback and communication
- Expanding room for manoeuvre and motivating employees
D3
Creating value with partners and suppliers
- Shaping partnerships strategically and ensuring sustainability
- Selecting, developing and retaining partners and suppliers
- Living partnership through dialogue
- Creating alternatives and strengthening resilience
- Utilising feedback and optimising collaboration
D4
Managing value creation, technology and resources
- Keeping specifications compact and increasing flexibility
- Optimising and digitising core processes
- Utilising data and accelerating decision-making
- Connecting and strengthening supply chains
- Applying technologies and driving innovation
E
Demonstrate impact
E1
Demonstrating impact on social interests
- Demonstrating and evaluating the impact on social interests
- Demonstrating the impact of suppliers and partners on social interests
- Presenting future viability based on the impact on social interests
- Ensuring communication and transparency on social impacts
- Reporting on laws and sustainability standards
E2
Demonstrating impact on environmental interests
- Demonstrating and evaluating impact on environmental interests
- Demonstrating the impact of suppliers and partners on environmental interests
- Presenting future viability based on the impact on environmental interests
- Ensuring communication and transparency on ecological impacts
- Reporting on laws and sustainability standards
E3
Demonstrating impact on economic interests
- Identifying and evaluating the impact on economic interests
- Demonstrating the impact of suppliers and partners on economic interests
- Presenting future viability from an economic perspective
- Presenting future viability based on the impact on economic interests
- Ensuring communication and transparency on economic impact
- Reporting on laws and sustainability standards
F
Master change
F1
Winning people for change
- Promoting a willingness to change and developing a positive mindset
- Telling the story of change and building the ability to change
- Living exemplary leadership and providing psychological safety
- Obtaining continuous feedback and making adjustments
F2
Empowering the organisation for change
- Planning and balancing change at an organisational level
- Defining and leading change processes
- Measuring and optimising the effectiveness of change (from the organisation's perspective)
- Reflecting and strengthening the capability for change in corporate culture
F3
Changing the organisation in context
- Designing and strengthening relationships in an organisational context
- Ensuring and adapting communication within the organisational context
- Identifying and using synergies in an organisational context
- Driving change in the value creation network
Excellence Framework Europe –
The Principles
Values and responsibility as the foundation of excellent organizations
The Excellence Framework Europe takes a holistic view of outstanding organizations – in their actions, their impact and their results. Excellence is not only reflected in success or in the perception of stakeholders, but above all in the consistent adherence to common principles and values.
European values as a basis
The European and global basic concepts of living together in freedom, self-determination and democracy form the ethical and social framework of the Excellence Framework Europe.
The central reference frameworks include:
Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union (Treaty of Lisbon)
European Convention on Human Rights
European Social Charter with 19 social rights
Directive 2000/78/EC – Equal Treatment Framework Directive
UN Global Compact (2000) – Principles for sustainable and socially responsible corporate governance
UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) (2015)
Self-commitment to lived values
Each organization is responsible for defining and transparently communicating its own lived values and principles framework. When evaluated according to the Excellence Framework Europe, for example in the context of award procedures, participating organizations consciously commit to complying with the principles and values that define Europe.
Further information on the principles of the Excellence Framework can be found in our brochure.
Download the brochure now.
Excellence Framework Europe –
The Hexagon
The model for lived excellence
The Excellence Framework Europe hexagon forms the heart of the framework. It describes the content and fields of action that excellent organizations consistently implement in order to clearly stand out from the crowd.
Six dynamically connected areas
The EFE hexagon is divided into six interconnected areas that influence each other and “pulse” in a coordinated rhythm.
It clearly shows what organizations actually DO to live excellence – practical, observable and transferable.
Overall, the hexagon includes:
6 areas of organizational excellence
20 sub-areas that specifically describe the actions of successful organizations
Further information and a detailed description of the hexagon areas can be found in our brochure.
Download the brochure now.
Excellence Framework Europe –
The Maturity Model
The path to objective organizational assessment
The EFE maturity model makes it possible to determine the maturity level of any organization – regardless of size, industry or management system used – easily, quickly and comprehensibly.
Holistic instead of formalistic
The focus is not on rigidly working through criteria, but on holistically classifying the organization into clearly defined, differentiated maturity levels. At the same time, strengths and development potentials become visible, which form a solid basis for targeted further development.
Five maturity levels with clear capabilities
The model distinguishes five organizational maturity levels. For each level, the organizational capabilities that must be mastered for the respective stage of development are described.
These capabilities include central topics such as:
Stakeholders
Employees
Culture
Leadership
Strategy
Structure
Results
Improvement
Success
Detailed information on the maturity levels and assessment criteria can be found in our brochure.
Download the brochure now.